You’ve likely heard whispers or maybe you’ve faced the headache yourself—the dreaded voltage regulator issue that can strike your Polaris Ranger out of the blue. It’s the sort of hiccup, often discussed in related threads and forums top contributors, that might have you furrowing your brow in confusion when your trusty ATV starts acting up. In the realm of off-roading adventures and durable workhorses, this trusty steed stands out, but it’s not immune to bouts of electrical gremlins. In this article, you’re going to get the lowdown on what these Polaris Ranger voltage regulator problems are, how they can manifest, and, crucially, what steps you can take to keep your Ranger running smoothly, avoiding the pitfall of being left stranded in the great outdoors.
Understanding the Voltage Regulator in Polaris Ranger
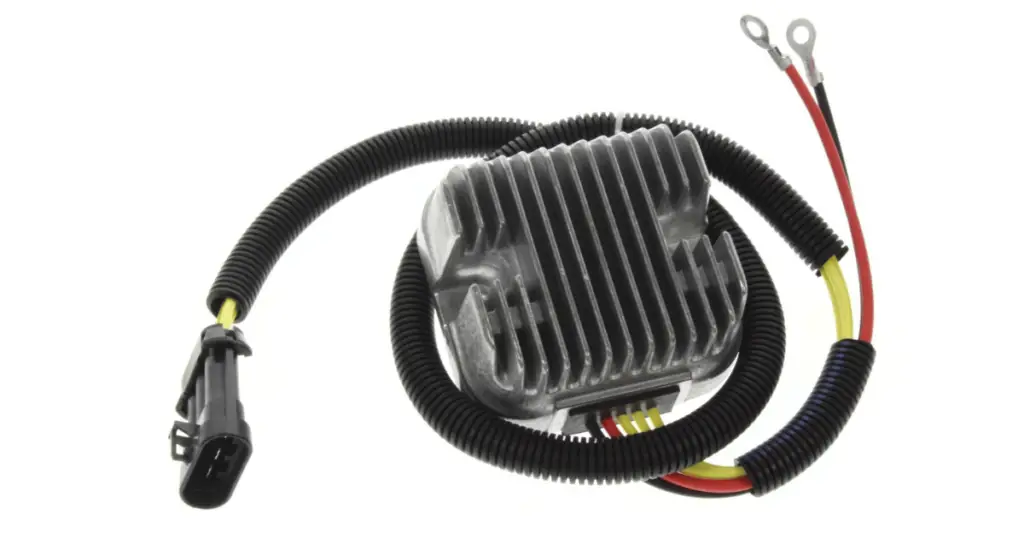

Function of the voltage regulator
Your Polaris Ranger, much like any other vehicle with an engine, uses a voltage regulator, a key component in managing both AC voltage and DC voltage, as a crucial part of its electrical system. Essentially, the voltage regulator’s job is to maintain a constant, safe voltage level within your vehicle’s electrical system. It’s vital for keeping the battery charged and ensuring that all the electrical components, including the fuel pump, receive the optimal level of power without risking overcharging or electrical damage.
Location and components of the voltage regulator
The voltage regulator in your Polaris Ranger is typically mounted on or near the vehicle’s radiator or along the chassis for better cooling, as it can get quite hot during operation. This component, crucial in the charging system, is fairly compact and is connected to your Ranger’s electrical system via various wires and connectors. Inside, the regulator comprises an array of circuits, heat sinks, and sometimes, cooling fins that aid in dissipating excess heat.
How the voltage regulator works in the Polaris Ranger
The inner workings of the voltage regulator are quite interesting. Your Polaris Ranger generates electrical power via the alternator, which converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical power for charging the battery and powering electrical components. As the engine speed changes, so does the output from the alternator, but your electrical system requires a steady voltage. This is where the voltage regulator comes in – it continuously adjusts the alternator output to maintain a constant voltage level, usually around 14 volts, to keep the battery charged and the electrical system running smoothly.
Common Symptoms of Voltage Regulator Failure
Battery overcharging or undercharging
If you notice that your Ranger’s battery, a good battery being essential, seems to be underperforming, it could be a telltale sign of voltage regulator failure. Overcharging can lead to a shortened battery life due to excessive wear and potential leakage or swelling. Conversely, undercharging means your battery isn’t getting the juice it needs, causing it to drain more quickly and lack the power to start your engine.
Electrical component malfunctions
When the voltage regulator isn’t doing its job, you might find that electrical components are either overworked or not getting enough power. This can manifest in troublesome operation of accessories, ignition problems, or even the refusal of certain electrical systems to turn on at all.
Flickering or dimming lights
Your lights are direct visual indicators of the health of your Ranger’s electrical system. Flickering or dimming headlights and dashboard lights could suggest fluctuations in the electrical supply, often pointing to a faulty voltage regulator.
Warning light indicators on the dashboard
Modern Polaris Rangers have built-in diagnostic systems that monitor electrical performance. If there’s an issue with the voltage regulator, you may find a warning light illuminated on your dashboard. While it’s not specific to the regulator alone, it’s a prompt for you to check the electrical system.
With all of this in mind, I’ll ask you the next question I think you should consider: How many miles will a Polaris Ranger last?
But which Ranger years are the worst?
Diagnosing Voltage Regulator Problems
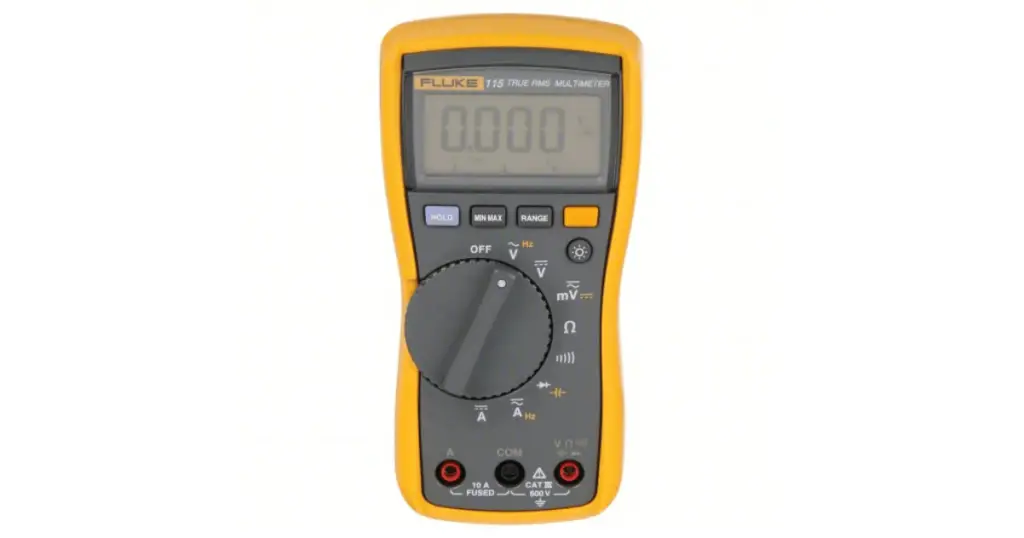

Steps to diagnose regulator issues
To pinpoint a faulty voltage regulator, you’ll want to start by inspecting your battery’s health, including checking for low voltage issues. If it seems fine, the next step is to run the engine and measure the voltage output at the battery terminals. The voltage should be within the normal range specified for your Polaris Ranger, typically around 14 volts. Significant deviations could indicate a regulator issue.
Tools needed for diagnosis
Get your hands on a reliable multimeter for measuring voltage, including checking the charge voltage, and you might also want to have a load tester to assess your battery’s health more thoroughly. These tools will be instrumental in diagnosing electrical issues and can save you from unnecessary part replacements.
Interpreting voltage readings
When using a multimeter, if you register a reading significantly above the 14-volt range when revving the engine, that suggests overcharging. If the reading is well below this level, the battery might be undercharged. An optimal reading should show minor fluctuations but stay relatively close to the expected 14 volts.
Consequences of Ignoring Voltage Regulator Failure
Potential damage to the electrical system
Ignoring signs of voltage regulator failure, such as high voltage or low voltage issues, is a bad idea as it can cause extensive damage to your Ranger’s electrical system over time Sensitive electronic components can be fried by unregulated high voltages, or left unable to function from insufficient voltage, leading to costly repairs.
Battery life degradation
A battery subjected to continuous overcharging or undercharging will undoubtedly see its lifespan significantly reduced. Replacing batteries more often than necessary is not only a hassle but also an avoidable expense.
Safety hazards
Electrical malfunctions are not something you want to ignore. These can lead to unpredictable behaviors in your vehicle’s operation, potentially putting you in hazardous situations, especially if critical components like headlights fail when you need them most.
Related: Polaris Ranger Turf Mode Problems Fixed
Troubleshooting Polaris Ranger Voltage Issues
Inspecting wiring and connectors for corrosion or damage
Start by giving your wiring and connectors a once-over. Look for signs of corrosion, loose fittings, or damaged wires. Issues here can hinder proper voltage regulation and mimic the symptoms of a bad regulator.
Checking the battery condition
Evaluate your battery’s state. Make sure it’s holding a charge and that there’s no visible damage or corrosion on the terminals. A dying battery can cause symptoms similar to voltage regulator issues.
Testing the alternator output
The alternator is the counterpart to the voltage regulator in your charging system. Test the alternator’s output to ensure it’s within the proper range. If the alternator is faulty, it could be the root cause of your electrical problems, not the regulator.
Replacing the Voltage Regulator
When to decide replacement is necessary
After thorough troubleshooting, if all signs point to the voltage regulator, it’s time for a replacement. It’s better to address this sooner rather than later to avoid additional system damage.
The replacement process
Replacing the voltage regulator, especially if you’re dealing with bad connections, is usually straightforward – disconnect the battery, remove the old regulator, ensuring you note where each wire was connected, and then install the new one in the same position, reconnecting the wires exactly as they were.
OEM vs. aftermarket voltage regulators
You’ll have to decide whether to go with an Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) or an aftermarket voltage regulator. OEM parts guarantee compatibility and reliability, while aftermarket options might offer a better price point or increased performance. Assess your needs and make an informed choice.
Upgrading the Voltage Regulator
Benefits of upgrading to a higher quality regulator
Upgrading to a higher-quality voltage regulator, perhaps even considering options like an RM Stator, might improve the performance and longevity of your Ranger’s electrical system. High-end regulators often feature better heat dissipation, more precise voltage control, and stronger construction.
Recommended products and manufacturers
Do some digging into brands that specialize in power sports electrical components. Look for manufacturers with solid reputations, positive reviews, and a track record of quality products.
Installation tips for upgrades
If you’re upgrading your voltage regulator, make sure you’re aware of the specs and installation requirements. Some high-performance regulators might need additional modifications or specific installation procedures. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure optimal performance.
Preventative Measures and Maintenance Tips
Regular inspection intervals
Set up a schedule to regularly inspect your Polaris Ranger’s voltage regulator and electrical system, including the charging circuit. This will help you catch any potential issues before they escalate into bigger problems.
Maintaining a clean electrical system
Dirt, mud, and moisture are enemies of electrical systems. Keep your systems clean to ensure good conductivity and reduce the risk of corrosion.
Ensuring tight connections and proper grounding
A good electrical system is only as good as its connections. Make sure all connections are secure and that the grounding points are free from rust or paint, which could interfere with the electrical circuit.
And, make sure you understand all of the check engine codes for when they appear:
Full Guide To Identifying Polaris Ranger Check Engine Codes
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Dealing with Voltage Regulators
Overlooking simple solutions
Before concluding that the voltage regulator is the culprit, check the basics – battery health, wiring, and connections, and ensure there’s no issue with the ground connector. These simple checks can save time and money.
Delaying repairs or replacement
Don’t put off fixing electrical issues. Delaying can compound the problems, potentially leading to more extensive and expensive repairs down the line.
Incorrectly diagnosing the issue
Be sure of your diagnosis before replacing parts. Misdiagnosing and subsequently replacing the wrong components can be frustrating and expensive. Take your time with the diagnosis or seek a second opinion if you’re unsure.
Navigating Warranty and Support Options
Understanding Polaris Ranger’s warranty
Familiarize yourself with the Polaris Ranger’s warranty conditions regarding the electrical system, including what’s covered and for how long. This knowledge is your friend if you’re facing voltage regulator problems while still under warranty.
Dealing with the dealer or service centers
If you’re not comfortable tackling electrical issues or if your Ranger is under warranty, it’s wise to let authorized dealers or service centers handle the diagnosis and repair.
What to do if your warranty has expired
Once you’re out of warranty, you have the flexibility to choose who works on your Ranger. Consider a trusted local mechanic with experience in power sports vehicles, or, if you’re mechanically inclined, take it as an opportunity to learn and repair it yourself.


